AC-Coupled vs DC-Coupled Battery Storage: The Pros and Cons
Choosing between AC coupled vs DC coupled battery storage can make or break your solar investment. This comprehensive guide breaks down the key differences between these two battery storage systems to help homeowners, solar installers, and energy professionals make informed decisions. AC coupled battery systems and DC coupled battery systems each offer distinct advantages for solar battery storage coupling, but they work in fundamentally different ways. Understanding these energy storage system types is crucial before investing thousands in a residential battery storage system.
Table of Contents
ToggleWe’ll examine how AC coupled and DC coupled systems operate, compare their efficiency levels and installation requirements, and outline the specific pros and cons of each approach. You’ll also discover which battery coupling option works best for different home setups and energy goals, giving you the knowledge to choose the right solar energy storage solution for your specific needs. However, one of the most common questions we hear at Eco Aspire Energy is: “What’s the difference between AC-coupled vs DC-coupled battery storage, and which one is better?”
If you’re comparing AC-coupled vs DC-coupled battery storage, you’re already on the right track. Both options have clear advantages, and the best choice depends on your existing system, budget, and energy goals. In this detailed guide, we’ll explain ac vs dc battery storage, break down the pros and cons, and help Australian homeowners make an informed decision.
What is AC-Coupled Battery Storage?
First things first, let’s clarify what AC-coupled battery storage means. In an AC-coupled system, the battery storage connects to the AC side of your solar setup. This typically involves using an AC-coupled battery inverter that works alongside your existing solar inverter. It’s like adding a separate battery system that communicates with your grid-tied solar panels through AC power. AC-coupled vs DC-coupled battery storage is a common debate, and AC-coupled systems are popular for retrofitting existing solar installations without major changes. In Australia, where solar adoption is booming, AC-coupled battery storage is often chosen for its flexibility.
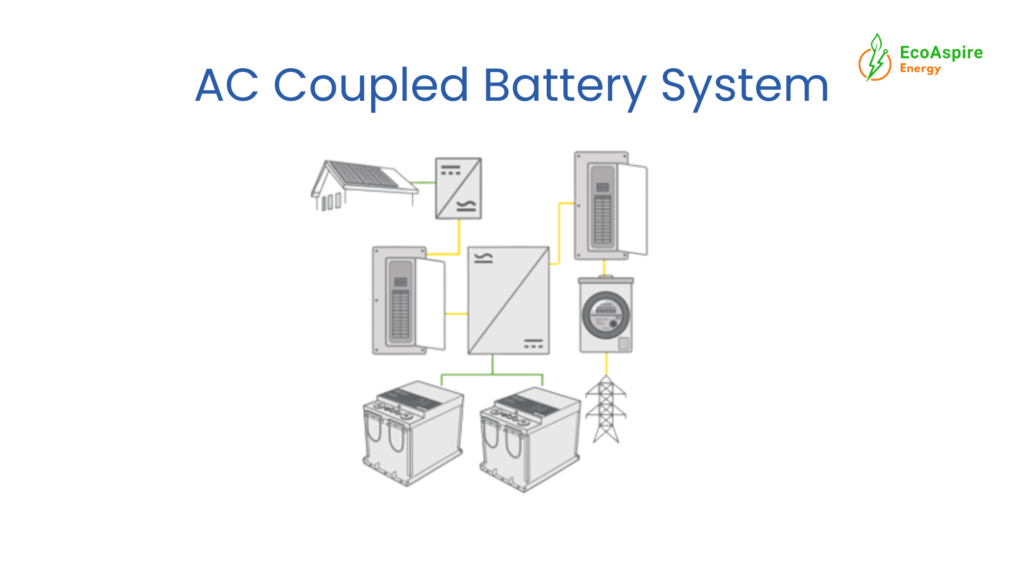
How AC-Coupled Battery Storage Works
- Solar panels produce DC electricity
- A solar inverter converts DC power to AC
- Your home uses the AC power
- Excess energy is converted back to DC via a battery inverter to charge the battery
Because of this setup, AC-coupled systems typically use two inverters, one for solar and one for the battery.
What is DC-Coupled Battery Storage?
On the flip side, DC-coupled battery storage connects directly to the DC side of your solar array. This means the battery charges straight from the solar panels before any conversion to AC power. A DC-coupled system usually requires a hybrid inverter that handles both solar and battery functions. DC-coupled vs AC-coupled battery storage differs in efficiency and setup, with DC-coupled often seen as more streamlined for new installations.
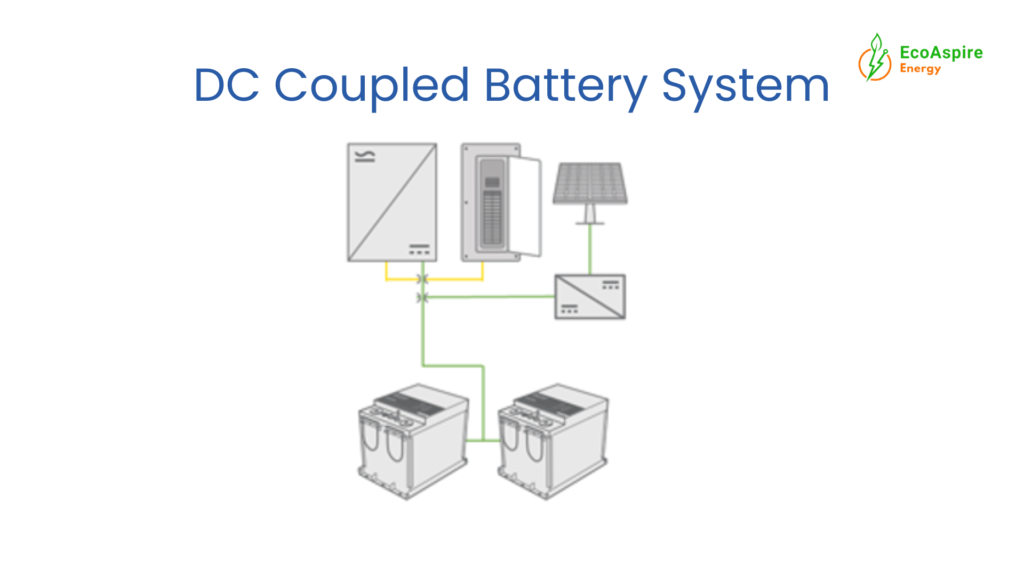
How DC-Coupled Battery Storage Works
- Solar panels generate DC electricity
- DC power directly charges the battery
- Stored energy is later converted to AC for home use
This setup typically uses a hybrid inverter, which manages both solar generation and battery storage.
AC Coupled vs DC Coupled: The Fundamental Differences
The distinction between AC-coupled and DC-coupled battery storage systems lies in their energy transmission mechanisms, system configurations, and conversion efficacy. Grasping these disparities is imperative for the selection of an optimal system for particular energy requirements.
1. Energy Flow Comparison
In AC-coupled systems, energy transitions from solar panels to an inverter, then to the AC bus, and ultimately to the battery storage system via a distinct inverter/charger. In contrast, DC-coupled systems facilitate direct energy transfer from solar panels to a charge controller and then to the battery bank. The inverter, drawing energy from the battery bank, supplies AC power. This dichotomy in energy transmission impacts system efficiency and complexity.
2. System Architecture Differences
AC-coupled systems exhibit modularity, facilitating expansion or modification. They comprise multiple components, including separate inverters for solar and storage. In contrast, DC-coupled systems present an integrated architecture, with solar generation and energy storage closely integrated. This integration simplifies system design but may restrict flexibility.
3. Conversion Efficiency Comparison
Conversion efficiency is a critical determinant of a battery storage system’s overall efficacy. AC-coupled systems, involving multiple conversions (DC to AC and AC to DC), are prone to higher energy losses. DC-coupled systems, with fewer conversion stages, potentially enhance overall efficiency.
4. Power Loss Analysis
An in-depth examination of power loss in both systems indicates that DC-coupled configurations generally exhibit an advantage due to fewer conversion stages. The actual efficiency gain, though, hinges on various factors, including the specific components employed and the system’s operational conditions.
In the selection between AC-coupled and DC-coupled systems, it is critical to consider these fundamental differences and their alignment with your energy storage needs and system specifications.
Pros and Cons of AC-Coupled Battery Storage
Now, let’s weigh the pros and cons of AC-coupled battery storage. We’ll keep it balanced so you can see why AC vs DC coupled battery storage is such a hot topic.
Pros of AC-Coupled Battery Storage:
- Easy Retrofitting: One of the biggest advantages of AC-coupled systems is that you can add battery storage to an existing solar setup without replacing your solar inverter. This makes it cost-effective for upgrades in Australian homes.
- Flexibility with Brands: AC-coupled battery storage allows you to mix and match components from different manufacturers, giving you more options for “ac vs dc battery” configurations.
- Grid Interaction: It excels in grid-tied systems, enabling features like demand response and easy integration with the Australian energy market.
Cons of AC-Coupled Battery Storage:
- Lower Efficiency: There’s a slight energy loss due to multiple conversions (DC to AC, then back to DC for storage), which might not be ideal for “ac vs dc coupled battery storage” efficiency seekers.
- Higher Complexity: More components mean more potential points of failure, and it might require additional wiring or inverters.
- Cost Over Time: While initial setup is cheaper, ongoing maintenance could add up, especially in humid Australian climates.
Pros and Cons of DC-Coupled Battery Storage
Switching gears to DC-coupled battery storage, here’s a look at its strengths and weaknesses. This is where “DC-coupled vs AC-coupled battery storage” really comes into play for performance-focused users.
Pros of DC-Coupled Battery Storage:
- Higher Efficiency: By connecting directly to the DC side, DC-coupled systems minimize energy losses, making them a top choice for “ac vs dc battery storage” efficiency in solar-rich areas like Australia.
- Simpler Setup: Fewer components mean less complexity, which is great for new builds or off-grid solar systems.
- Better for High Loads: It handles peak loads more effectively, ideal for homes with high energy demands or electric vehicles.
Cons of DC-Coupled Battery Storage:
- Higher Upfront Costs: DC-coupled battery storage often requires a new hybrid inverter, bumping up the initial investment compared to AC-coupled options.
- Less Flexible for Retrofitting: If you already have a solar system, switching to DC-coupled might mean overhauling your setup, which isn’t always practical in Australia.
- Dependency on Inverter: You’re tied to the inverter’s capabilities, limiting brand choices for “ac vs dc battery” expansions.
AC-Coupled vs DC-Coupled: Which is Best?
So, AC-coupled vs DC-coupled battery storage – which one wins? It really depends on your needs! For existing solar owners in Australia looking for a quick, affordable upgrade, AC-coupled battery storage might be the way to go. It’s perfect for “AC-coupled vs DC-coupled battery storage” scenarios where flexibility trumps efficiency.
On the other hand, if you’re building a new system or prioritising maximum energy savings, DC-coupled could be better. Think about factors like your location (e.g., “solar battery storage Australia” trends in Sydney vs. Perth), budget, and whether you want off-grid capabilities. Both “ac vs dc battery storage” options support renewable energy goals, but consulting a pro ensures the best fit.
In Australia, where government incentives like the Small-scale Renewable Energy Scheme boost solar adoption, choosing the right battery storage can maximise your returns. Keywords like “best battery storage for solar panels Australia” point to hybrid systems that blend both worlds.
So, Which is Right for You? A Summary Table
To make it easy, here’s a quick comparison table to help you decide.
Feature | AC-Coupled Battery Storage | DC-Coupled Battery Storage |
Best for | Retrofitting batteries to existing solar | New solar + battery installations |
Energy Efficiency | Good (89-94%) | Excellent (94-98%) |
Retrofit Cost | Lower | Higher (requires new inverter) |
New Install Cost | Higher (two inverters) | Lower (one hybrid inverter) |
Backup Redundancy | Excellent (two inverters) | Good (single point of failure) |
System Flexibility | Excellent (works with any solar system) | Good (requires brand compatibility) |
Upgrade Options | Easy | Sometimes restricted |
Cost Analysis: Initial Investment vs Long-Term Returns
An examination of the cost-effectiveness of AC-coupled and DC-coupled battery systems necessitates a dual perspective: the initial expenditure and the subsequent financial benefits. This scrutiny is imperative for a well-informed choice between the two systems.
Equipment and Installation Costs
The initial expenditures for AC-coupled and DC-coupled systems exhibit marked disparities. AC-coupled systems incur higher installation costs due to their complex architecture, necessitating multiple conversion stages. In contrast, DC-coupled systems present with lower upfront costs, facilitated by their streamlined design that directly connects the battery to the DC bus.
- AC-coupled systems: Higher equipment and installation costs due to complexity.
- DC-coupled systems: Lower initial costs due to simplified design.
Operational Efficiency and Energy Savings
Operational efficiency emerges as a critical factor in the cost analysis. DC-coupled systems generally exhibit superior efficiency, minimizing conversion losses by leveraging DC power directly. In contrast, AC-coupled systems, with their increased conversion steps, incur higher energy losses.
Key efficiency considerations:
- DC-coupled systems: Higher efficiency, less energy loss.
- AC-coupled systems: Lower efficiency, more conversion losses.
Maintenance and Replacement Expenses
Maintenance costs significantly influence the overall cost analysis. AC-coupled systems, with their complex architecture, may necessitate more frequent maintenance and potentially higher replacement costs over time. In contrast, DC-coupled systems, with their simpler design, may reduce the necessity for recurrent maintenance
Return on Investment Calculations
To ascertain the return on investment (ROI), we must integrate both the initial costs and the ongoing savings or expenses associated with each system. While DC-coupled systems may offer superior efficiency and lower maintenance costs, the initial cost savings or additional expenses must be considered in ROI calculations.
ROI considerations:
- Initial investment costs.
- Ongoing energy savings.
- Maintenance and replacement expenses.
In conclusion, both AC-coupled and DC-coupled systems present unique cost implications. A detailed analysis of initial investment versus long-term returns is indispensable. By examining equipment costs, operational efficiency, and maintenance expenses, we can make a more informed decision that aligns with our financial objectives.
Why Choose Eco Aspire Energy?
At Eco Aspire Energy, we specialise in high-quality solar and battery storage solutions tailored to Australian homes and businesses. Our expert team helps you choose between AC-coupled vs DC-coupled battery storage with honest advice, professional installation, and long-term support.
Remember, the best choice aligns with your lifestyle and goals. If you’re in Australia, consider local factors like feed-in tariffs and weather patterns. For more tips on solar battery storage in Australia, contact us for a free consultation.
👉 Contact Eco Aspire Energy today and take control of your energy future.
FAQ
Q: What is the main difference between AC-coupled and DC-coupled battery storage systems?
A: The distinction between AC-coupled and DC-coupled systems resides in their connection to the electrical grid or solar panel systems. AC-coupled systems interface with the grid or solar systems via an AC link, whereas DC-coupled systems directly connect to the DC bus of the solar panel system.
Q: What are the advantages of AC-coupled battery systems?
A: AC-coupled systems boast flexibility, modularity, and the ability to retrofit existing solar panel systems. Their redundancy benefits also provide blackout protection features.
Q: What are the disadvantages of AC-coupled battery systems?
A: AC-coupled systems incur conversion losses, exhibit increased complexity, and entail higher costs. They necessitate more maintenance due to their intricacy.
Q: What are the advantages of DC-coupled battery systems?
A: DC-coupled systems showcase enhanced efficiency, streamlined system design, and cost-effectiveness for new installations. They also facilitate clipping recapture, boosting overall system efficiency.
Q: What are the disadvantages of DC-coupled battery systems?
A: DC-coupled systems face limitations in flexibility, present upgrade challenges, and are susceptible to single points of failure. Compatibility issues can hinder the integration of disparate components.
Q: How do I choose between AC-coupled and DC-coupled battery storage systems?
A: Selecting between AC-coupled and DC-coupled systems hinges on your specific requirements, encompassing energy storage needs, budget, and existing solar panel setup. We advocate for a thorough evaluation of efficiency, cost, and complexity to guide your decision.
[Disclaimer: The information provided in this article is for educational and informational purposes only. While efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, the author makes no guarantees regarding completeness or correctness. Please consult a qualified battery and solar installer to ensure that the information is current, accurate, and compliant with applicable regulations in your jurisdiction.]

